| |
| |
Caption: Board of Trustees Minutes - 1926
This is a reduced-resolution page image for fast online browsing.
EXTRACTED TEXT FROM PAGE:
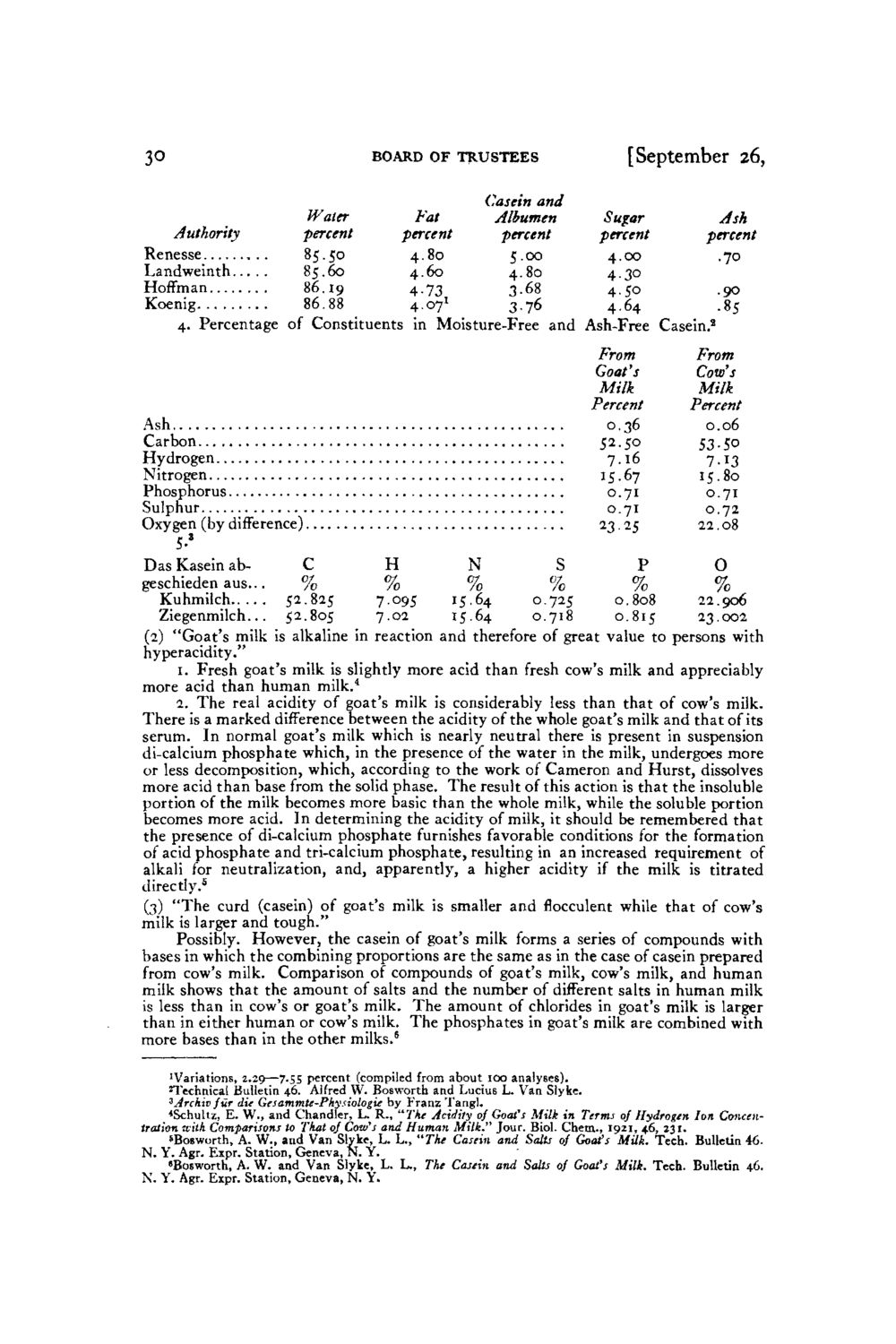
3° BOARD OF TRUSTEES [September 26, Casein and Water Fat Albumen Sugar Ash Authority percent percent percent percent percent Renesse 85.50 4.80 5.00 4.00 .70 Landweinth 85.60 4.60 4.80 4-3° Hoffman 86.19 4-73 3-68 4.50 .90 Koenig 86.88 4071 3.76 4.64 .85 4. Percentage of Constituents in Moisture-Free and Ash-Free Casein.2 From From Goat's Cow's Milk Milk Percent Percent Ash 0.36 0.06 Carbon 52-5° 53-50 Hydrogen 7-i6 7.13 Nitrogen 15.67 15.80 Phosphorus 0.71 0.71 Sulphur 0.71 0.72 Oxygen (by difference) ^i^S 22.08 5-* DasKaseinabC H N S P O geschiedenaus... % % % % % % Kuhmilch 52.825 7.095 15.64 0.725 0.808 22.906 Ziegenmilch... 52.805 7.02 1 5 6 4 0.718 0.815 23.002 (2) "Goat's milk is alkaline in reaction and therefore of great value to persons with hyperacidity." 1. Fresh goat's milk is slightly more acid than fresh cow's milk and appreciably more acid than human milk.4 2. The real acidity of goat's milk is considerably less than that of cow's milk. There is a marked difference between the acidity of the whole goat's milk and that of its serum. In normal goat's milk which is nearly neutral there is present in suspension di-calcium phosphate which, in the presence of the water in the milk, undergoes more or less decomposition, which, according to the work of Cameron and Hurst, dissolves more acid than base from the solid phase. The result of this action is that the insoluble portion of the milk becomes more basic than the whole milk, while the soluble portion becomes more acid. In determining the acidity of milk, it should be remembered that the presence of di-calcium phosphate furnishes favorable conditions for the formation of acid phosphate and tri-calcium phosphate, resulting in an increased requirement of alkali for neutralization, and, apparently, a higher acidity if the milk is titrated directly.5 (3) "The curd (casein) of goat's milk is smaller and flocculent while that of cow's milk is larger and tough." Variations, 2.29-^7.55 percentcasein of from about 100forms a series of compounds with Possibly. However, the (compiled goat's milk analyses). bases in which the combining proportionsand Lucius L. Van in the case of casein prepared ^Technical Bulletin 46. Alfred W. Bosworth are the same as Slyke. from cow's milk.Gesammte-Pkysiologie compounds of goat's milk, cow's milk, and human zArckiv fur die Comparison of by Franz Tang]. milk shows that the amount of L. R., "The Acidity of Goafsdifferent saltsoj Hydrogen Ion Concen<Schultz, E. W., and Chandler, salts and the number of Milk in Terms in human milk tration aitk Comparisons or That of Cow's and Human Milk." Jour. Biol. Chem., 1921, 46,is larger is less than in cow's to goat's milk. The amount of chlorides in goat's milk 231. than in either A. W., and Van Slyke, L. The "The Casein and goat's milk are combinedBulletin 46. sBosworth, human or cow's milk. L., phosphates in Salts of Goafs Milk. Tech. with N. Y. Agr. than in the Geneva, N. Y. more basesExpr. Station,other milks.6 "Bosworth, A. W . and Van Slyke, L. L., The Casein and Salts of Goat's Milk. Tech. Bulletin 4.6. N. Y. Agr. Expr. Station, Geneva, N. Y.
| |